Polyester Fiber
 |
| Polyester Fibers |
The very first polyester fiber, Terylene, had been produced in Britain. It was very first introduced in the particular United States in 1951 by DuPont.Polyester’s outstanding moist and dry resiliency of polyester plus its excellent dimensional stability after temperature setting caused it to be a good and instant favorite. Occasionally referred to as the workhorse fiber, polyester is amongst the most broadly used synthetic fiber. Polyester filament type is extremely flexible its particular staple type could be mixed with many additional fibers, contributing appealing properties to the blend without wrecking the ones through the other fibers. Polyester’s versatility within blending is its special advantage. Today, polyester is a widely used fiber on the planet. The polyester polymer is endlessly engineerable, with many physical and chemical variants possible. Modified fibers improve polyester’s efficiency. The standard circular shape of polyester fiber can be modified easily to other shapes, for different attributes. High-tenacity staple polyester can be utilized in durable-press fabrics to strengthen cotton fibers destabilized by finishing. Additionally, polyesters possess the hand and absorbency more like the natural fibers. The particular properties of polyester are listed below in Table 1.
Physical Structure of Polyester
Polyester fibers are produced in many sorts. Filaments are higher or regular-tenacity, brilliant or delustered, white-colored or solution-dyed. Delusterant makes a speckled microscopic appearance. Delustered staple fibers are usually available in the range of deniers. They may become regular, low-pilling, or even high-tenacity. Polyester will be not as clear as nylon fibers. It is white-colored, so fibers usually need not end up being bleached. Nevertheless, brighter types of polyester fibers have optic whiteners added to the fiber-spinning option. Normal polyester fibers are usually smooth rodlike fibers with a rounded cross-section. Cross-sectional shapes include circular, trilobal, octolobal, oblong, hollow, voided, hexalobal, and pentalobal (star-shaped).
Chemical Composition plus Molecular Arrangement associated with Polyester Polyester fibers created fibers within which the fiber-forming substance is any kind of long-chain synthetic polymer made up associated with at least eighty-five pct by bodyweight of the ester of a replaced aromatic carboxylic acid solution, including, but not limited to, replaced terephthalate units, plus para-substituted hydroxybenzoate units.
 |
| Chemical Composition and Molecular Arrangement of Polyester |
Within which the fiber is formed simply by the interaction associated with two or a lot more chemically distinct polymers (of which not one exceeds 85 % by weight), plus contains ester group as the dominating functional unit (at least 85 % by the weight associated with the total plastic content from the particular fiber), and which usually, if stretched the minimum of one hundred percent, durably plus rapidly reverts to its unstretched size when the pressure is removed, the particular term elasterell-p might be used because of a generic explanation of the fiber.
Polyester fibers are manufactured from terephthalate polymers: polyethylene terephthalate (PET), poly 1, 4 cyclohexylene-dimethylene terephthalates (PCDT), polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), plus polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT). While the qualities of every plastic differ, generally the particular variations are small and do not lead to noticeable modifications in consumer overall performance. These polymers might be homopolymers or even copolymers. Most copolymers are pillresistant, lower-strength staple fibers utilized mainly in knits, blends, and carpets and rugs. Polyester fibers have got straight molecular chains that are loaded closely together and are also well oriented, along with strong hydrogen bonds.
Properties of Polyester
Polyester’s performance in apparel and interiors is summarized in following Table 2.
 |
| Table 2. Summary of the Performance of Polyester in Apparel |
Aesthetic
Polyester has variable looks that are quickly altered by choosing appropriate fiber adjustments or by the particular choice of wool or fabric framework or fabric coatings. Polyester fibers mix well, maintaining a good all-natural fiber look and consistency, with the advantage of easy treatment for apparel plus interiors. As the particular fabrics look such as the natural fiber within the mix, their improved look retention during make use of and care plainly illustrates the incident of polyester. Thick-and-thin yarns of polyester and rayon provide a linen change to apparel plus interior fabrics. Wool-like fabrics are discovered in both summer-weight and winter-weight match fabrics. Trilobal polyester fibers grew from research with the silk finishing business to build upward a made filament with the visual properties of cotton. The initial qualities of silk- liveliness, suppleness, and hang of the material; dry tactile hands; and good addressing power of the particular yarns-result from (1) silk’s triangular form; (2) its good denier per filament; (3) its reduce, bulky yarn plus fabric structure; plus (4) its extremely crimped fabric framework. Researchers applied these types of leads to polyester. Trilobal silklike polyesters are made into fabrics and prepared by a silk-finishing treatment with caustic soda creating the thinner, less standard fiber, yarn, or even fabric without essentially changing the fiber. Polyester microfibers are usually particularly suited to high-fashion apparel plus interiors due to their versatility and durability. Designers find the particular microfibers’ drape plus hand exciting plus challenging. Consumers voluntarily pay the extra cost for microfiber products. Microfibers produce softer and a lot more drapeable materials than conventional materials. Below Figure 1, illustrates the distinctions among fiber dimensions. Components of polyester microfibers, both polyester, and mixes with other materials, include coats, fits, blouses, dresses, energetic sportswear, wall covers, upholstery, sleeping handbags, tents, filters, plus toweling. These really fine fibers show unparalleled softness, fluidity, drape, and look. Shin-gosen polyesters are usually the most silk-like of the fine polyesters because of a result associated with slight irregularities together the fiber. A few modifications blend the microchannel using the trilobal cross-section; other people have tiny micro craters along the fiber’s surface. The methods used to create the microfibers plus shin-gosen fibers are usually similar, however, not similar, and the resulting fibers have somewhat different performance plus look characteristics.
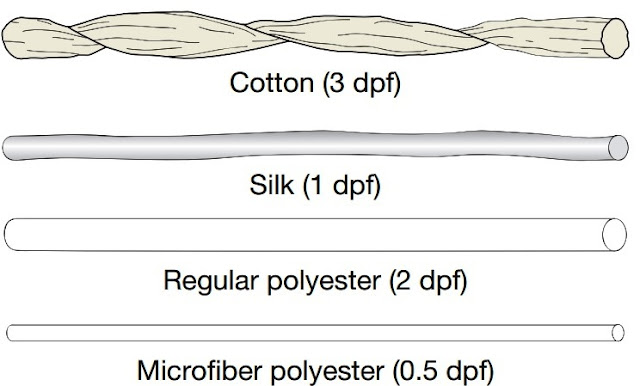 |
| Fig 1. Comparison of fiber diameter cotton, silk, regular polyester, and microfiber |
Durability
Polyester’s durability is outstanding. The abrasion level of resistance and tenacity associated with polyester is outstanding. Wet strength will be comparable to dried-out strength. The higher strength is created by hot drawing to develop crystallinity through increasing the particular molecular weight.
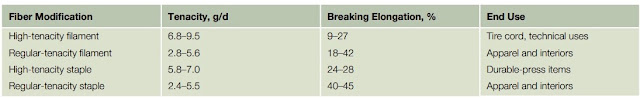 |
| Table 3. Performance Aspects of Modified Polyester Fibers |
Table 3, shows the variability of breaking tenacity with ending use. The particular tougher fibers are drawn more; their elongation is lower than that of the weaker fibers. This is especially dramatic in the case of partly oriented filament fibers that are sold to manufacturers who draw them more throughout the creation of textured yarns. Their tenacity is 2. 0 to 2. 5 g/d, lower power than staple fibers with an elongation exceeding that of other fibers, 120% to 150%. Marketed in yarn form, these polyesters are known as partly oriented yarn (POY). Elongation is slimmer than that of other synthetic fibers-a positive feature when blended with natural fibers. Because of its better sunshine resistance, polyester frequently occurs in ending utilizes in which sunshine resistance is necessary for durability, such as seatbelts, tarpaulins, and vehicle decorations.
Comfort
Polyester has low or poor comfort properties. Its absorbency is also poor, 0. 4% to 0. 8%. Poor or low absorbency lowers the comfort factor of skin-contact apparel and upholstery. Woven materials made from circular polyester fibers can be very unpleasant in warm, damp weather. Moisture will not escape easily from between the skin and the fabric, making the fabric feel advanced and clammy. Ease and comfort can be enhanced by using mixes with absorbent fibers or comfort-modified fibers, a thin and open fabric construction, spun-not filament-yarns, trilobal rather than circular fibers, and surface finishes that absorb, or wick, moisture. Soil-release finishes improve the wicking characteristics of polyester, thus bettering material breathability and comfort. Finishes and fiber modifications also improve the comfort of polyester. Blends of polyester and cotton are more comfortable in humid weather than are 100% polyester fabrics. Moisture is wicked along the outer surface of polyester fibers to the fabric surface, where it evaporates. Polyester is long-lasting when wet, so the fabric does not mat. Polyester is light in weight and dries quickly. Polyester displays moderate thermal preservation. It is generally less comfortable than wool or fat for cold-weather wear. Blends made of wool successfully improve comfort. Polyesters have already been specifically engineered for fiberfill. Fiber adjustments (hollow fibers, binding staple, and crimped fibers) perform very well. Their low absorbency makes polyester more vulnerable to stationary problems than other fibers in the heat-sensitive group. The particular static potential of polyester is reduced by modifying the fiber’s cross area, incorporating water-absorbing substances in the dissolve before extrusion, or adding topical ointment finishes such as soil-release and antistatic compounds. Cross-sectional adjustments may incorporate substances that create a porous fiber surface that traps dampness. Other cross-sectional adjustments expand the surface area per device mass ratio, thus slightly increasing the absorbency. The specific gravity of polyester fibers ranges from 1. 22 to 1. 38. Hollowed-out variants for fiberfill are lower in density. The lower density and specific gravity mean that polyester products consider less than similar products made of natural or regenerated fibers.
A good antistatic bicomponent core-sheath fiber combines the polyester core along with a softer polyester copolymer sheath that will be impregnated with carbon-black particles. As small as 2% associated with the fiber within a blend considerably reduces static accumulation. It is utilized within carpeting and furniture, filters, protective coats, felts, electrical parts, ropes, along with other programs in which stationary buildup can become hazardous or irritating.
Stretch polyesters are usually available. Elasterell-p will be a generic subclass of the polyester which will be based on biotechnology as well because the fermentation is associated with corn glucose. In comparison to nylon, the manufacturing of elasterell-p (also known as PTT or Triexta™) utilizes 30% less power and emits 63% less greenhouse gasoline. It can become stretched a minimal of 100% along with excellent recovery. This has good tenaciousness and is a long-lasting and easy treatment having a pleasing hand. It could become dyed easily plus heat-set. Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) has the particular ability to extend 10% to 15% with good recuperation. This is considerably better compared to that of normal polyester. PTT materials are durable, simple care, soft, possess good bulk, plus dye easily. Along with better stretch plus softer hand, the particular stretch polyesters are usually perfect for many clothing products including underwear, hosiery, active sportswear, and underwear. PTT or Triexta™ will be commonly present within carpets under the particular trade name Sorona™. Carpets made associated with this fiber are usually less resilient compared to nylon, but much softer. Their luster will be more like that will of nylon. Carpets and rugs are stain-proof and hydrophobic. Preferably, these carpets function best in reasonable traffic areas. Triexta™ can also become used in auto carpeting, upholstery, plus window blinds.
Appearance Retention
Polyester has high surface retention. Polyester fiber has magnificent resiliency. It (resiliency) refers to the manner and extent of recovery from deformation. Polyester has a high flexible recovery rate with low elongation, a key factor for apparel and interiors. When only small deformations are participating, as in wrinkling, polyester recovers better than nylon. This recovery is comparable to that of wool at higher elongations, which helps make clear the achievements of polyester and wool mixes. Nylon exhibits better recovery at higher elongations, therefore it performs better in products that are subject to better elongation-hosiery. For example, see below Table 4.
 |
| Table 4. Tensile Recovery from Elongation |
Polyester has a benefit over wool in many uses since wool has bad wrinkle recovery when wet. In high humidity, polyester materials do not reduce and are extremely proof of wrinkling. Nevertheless, when polyester products wrinkle and where wrinkles are arranged by body warmth and moisture, pushing might not take them off. Excellent resiliency makes polyester especially great for fiberfill in quilted materials such as quilts, bedspreads, parkas, and robes, and cushioning for furniture, futons, and mattresses. In case the fiber is flattened on one side or made asymmetrically, it requires a limited spiral curl of outstanding springiness. Fiberfill of a mix of fiber deniers gives different levels of support. Lumpiness in pillows can be prevented by running hot fine needles through the batt to spot-weld the fibers to each other. Fiber-fills with one, four, 7, or more hollowed-out channels are available (see below Figure 2).
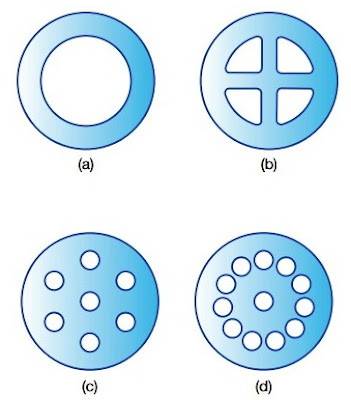 |
| Fig 2. Hollow polyester fibers |
To summarize, the resiliency of polyester is outstanding; it is resistant to wrinkles and, when wrinkled, it recovers well whether moist or dry. Flexible recovery is high for most outfits items. The dimensional stability of polyester is high. Whenever properly heat-set, it retains its size. It can be permanently creased or pleated. Pilling was a severe concern with fabrics made using unmodified polyester. Low-pilling fibers reduce the condition and are well suited for use in blends. The completing process of singeing also helps control pilling.
Care
Polyester is an easy-care machine wash or absorbing powder cleaning. Polyester has revolutionized consumer laundering. This trend occurred because of heat settings and the development of durable-press or wrinkle-resistant finishes. Care instructions for polyester/cotton durable-press fabrics are relatively simple: Wash in warm water; machine-dry with medium warmth; remove promptly when dry; hang; and jazz up with a steam metal if necessary. The particular wonderful abrasion level of resistance and tenacity and benefit elongation of polyester is the same whether the fabric is damp or dry. The particular low absorbency of polyester (0. 4%) means it is resistant to waterborne stains and is quick to dry. The excellent resiliency of polyester keeps it looking good during use and minimizes wrinkling during care so only light pushing may be expected. Because of warmth setting, dimensional balance and form preservation are. Warm-water cleaning is usually recommended to minimize wrinkling. Very hot water may give rise to wrinkling and color loss. However, warm water (120° F to 140° F) may be required to remove oily or oily unsightly stains or built-up body soil. Polyester is oleophilic so it retains oily ground. A familiar example of this is a ring around the collar. In polyester or polyester/cotton mix shirts, the ground usually responds to pretreatment before washing. The oleophilic character of polyester may lead to the redeposition of oily soil on fabrics, making them look dingy. Luckily, polyester is not the color scavenger that nylon is. Soil release finishes improving soil removal. An additional problem with polyester, especially noticeable with apparel, is microbial odor. This problem occurs when the ground has built on the fabric, promoting bacterial growth and odor. Use of hot-water wash, such laundry agents as borax, which reduces odor, or whitening to get rid of the ground buildup and destroy the bacteria reduce odor. Several liquids concentrate on odor elimination. Antibacterial modifications and finishes also reduce odor. Polyester materials are resistant to acids and alkalis and can be bleached with chlorine and oxygen bleaches. Polyester fibers are resistant to natural attack and also to sunshine damage, especially essential for sheer blind casement fabrics.
Sustainability of Polyester
Numerous sustainability issues that will be discussed concerning nylon also apply to polyester. See the particular earlier discussion within this chapter. Nonetheless, several major distinctions exist. The manufacturing of polyester utilizes less energy compared to the production associated with nylon, but a lot more energy compared to the production of natural cotton. Polyester uses the small amount associated with water during production. Some polyester is made along with chemicals that consist of heavy metal plus toxic compounds that will contaminate water plus soil, and possess a long-term effect on the atmosphere. Polyester is thoroughly recycled using possibly mechanical or chemical substance processing. In mechanized recycling, post-plus pre-consumer waste through bottle-grade, not fiber-grade, polyester is utilized. Chemical recycling begins with polyester clothing or products, the fiber-to-fiber process, to create better high-quality polyester fibers. Fiber-to-fiber recycling is a lot more sustainable since this is a closed-loop system and absolutely nothing leads to landfills. Production of reused polyester creates substantially less environmental air pollution compared to virgin mobile fibers made through new raw components. Air pollution will be reduced by as much as 85%. Challenges that had been overcome in the particular production of reused polyesters included reaching appropriate amounts of chastity of the polyester polymer and increasing spinning methods to make fibers associated with appropriate quality along with a comfortable hand. Current research on bleach dyed plus printed fabrics might increase the recyclability of polyester clothing and interior fabrics. Research into bioengineered and bio-based polymers may replace a huge percentage of the particular synthetic chemicals presently utilized in the particular production of polyester. Products produced from recycled polyester include apparel plus carpeting. For consumers such as these products, however, the price is normally greater than that for virgin-fiber products.
Uses of Polyester
Polyester is the most widely used produced fiber in the United States. It is crucial in woven materials for apparel and interiors. Polyester filament yarns may be used in a single or both directions of a fabric. Frequently, unique yarns blended with cotton or bamboo fibers are finished to be durable presses. Blended fabrics are attractive, durable, and comfortable (except in very hot and humid conditions), maintain their appearance well, and are easy to care for. Their excellent performance contributes to their widespread use and continued recognition. Woven fabrics are utilized in top-weight and bottom-weight apparel, linens, blankets, bedspreads, drapes and draperies, bed mattress ticking, table sheets, and upholstery materials. Filaments are utilized in sheer curtains, where their excellent light resistance and fine denier get them to be particularly ideal for ninon and marquisette. Another important use of polyester is in knitted materials. Polyester, as well as polyester/ natural cotton blend yarns, is used. Knit materials of polyester wear well, are comfortable, retain their appearance well, and are easy to care for. The particular first use of polyester filaments was in knit t-shirts for men and blouses for women. The use of filament polyester increased tremendously when distinctive yarns were developed.
Both smooth and textured filaments are utilized in such career clothing as uniforms and such inside textiles as warp-knit upholstery and window-treatment fabrics. A third important use of polyester is within fiberfill. Used in pillows, comforters, bedspreads, furniture padding, placemats, winter apparel, resting bags, and cushions, polyester dominates the market. Other fiberfill substances include down, feathers, and acetate. The polyester used for fiberfill is made for resiliency and loft. The durability, comfort, and easy care also make it appropriate for this finish use. Fiberfill is not noticeable during use-but poor performance shows up in lumpy products or hollow areas. Nonwoven or fiber web fabrics are a fourth important use of polyester. Nonwoven fabrics are utilized as interfacings or interlinings, pillow covers, and furniture and bed mattress interlinings. They are utilized where the sturdiness of rayon is inadequate and where absorbency is not needed. Olefin is a strong rival in many specialized uses. Nonwoven polyester is utilized in medical soft-goods applications including nonabsorbent bandages and pads for coronary heart monitors. Other fiber web products include base fabrics for laminates and coatings. A tire cord is the fifth important use of polyester. Polyester tires do not flat place as nylon wheels do. A small percentage of carpets and rugs are polyester; they have a much softer hand than most nylon carpets. Polyester carpets are not as traffic-resistant as nylon carpets. Nevertheless, polyester carpets perform well in low-use areas like rooms. Polyester carpets experience from a strolled-down look after an interval of wear in heavy-traffic areas. Heat-setting the fibers minimize the problem. Some polyester carpet fiber has improved resistance to matting and mashing. Polyester is utilized for many other consumer and technical utilizes: pile fabrics, tents, ropes, cording, angling line, cover stock for disposable pampers, garden hoses, sails, seatbelts, filters, materials used in street building, seed and fertilizer bags, stitching threads, and synthetic arteries, veins, and hearts. Polyester is utilized in replacement bloodstream, heart valves, and support tissue. The study continues to increase technical applications. For example, a brand new polyester, polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) is a high-performance, high-strength polyester used in technical hoses, devices, tire cords, or another cordage, sailcloth, engineered reinforcements, thin fabrics, and felts. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) has good dimensional firmness with low elongation and low shrinkage.


.png)









0 comments:
Post a Comment